Cloud Architecture (Unit 1)
Cloud Architecture (Unit 1)
Cloud Architecture - Unit 1 - CA - SRMIST Syllabus - Short Notes
Internet vs Cloud
Definition Points (Characteristics)
- On-Demand - Provide Service when needed.
- Pay-as-you-go pricing - Pay only for services you use.
- Broad Network Access - Resources from any device - phone, laptop, tab, etc.
- Scalable - More customers do not affect efficiency.
- Resource Pooling - Resources that are idle are all considered for cloud resources pool.
Components
- Client Computers
- Thick Clients
- Thin Clients
- Data Center
- Distributed Servers
Convergence
Resource Sharing
- Compute - Processing workload.
- Storage - Save & Store data.
- Database - Storage of structured & unstructured data sets.
- Network - Provide connectivity to every other resource type.
Deployment Model
- Private - VPC externally or internally hosted for a specific organization or group.
- Public - Externally hosted for anyone to use.
- Hybrid - A combination of all other models (usually used in IT companies)
- Community - Hosted for the exclusive use of a community. (private<community<public)
Service Model
- SaaS
- PaaS
- IaaS
Enabling Techniques
- Grid Computing - Distributed set of computing.
- Utility Computing - Pay as per services used.
- Internet - Connectivity of the cloud service on a global scale.
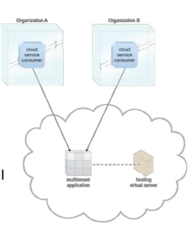
- Multi-tenancy - Multiple users can use the service at the same time.
- Web 2.0 - World Wide Web
- SOA - Architecture based on services.
- Automation - Without human intervention or hindrance.
- Virtualization - Splitting hardware or software resources for multiple instances.
- Hardware
- Software
- Full
- Para
Benefits
- Profitable - Pay as you go, which makes it cost-effective.
- Scalable - More users won't make it less effective.
- Accessibility - Available around the world, either on a phone or PC, or laptop.
- Security - Encryption methods to safeguard data.
- Productivity - Less downtime, more productivity.
- Round-the-clock service - Reason for less downtime.
- Latest Software - Better software for execution.
- Speed - Accessible almost instantly.
- Teamwork - Less time spent on planning finance for required resources.
Challenges
- Security - Open-source leads to vulnerable data.
- Management of speed - Cloud can be expensive with improper management.
- Lack of expertise - Not enough cloud experts.
- Governance - Native governance laws as it is in their initial stages yet,
- Compliance - Flexibility of movement from cloud to cloud.
- Managing multiple clouds - Hybrid cloud management becomes an issue.
- Performance Levels - Multi-tenancy must not be an issue.
- Building VPC - Hard to build a dedicated VPC.
- Portability - Migration to other CSPs (Cloud Service Providers) must be easy.
- Service Quality
- Interoperability
- Availability & reliability
Cloud Architecture
Benefits
- Solves latency issues
- Reduces cost of operation
- Easy to scale up business
- Flexibility feature
- Better disaster recovery
- Up-to-date services
- Remote working & team-collaboration
Challenges
- Service Availability
- Data Privacy
- Bottlenecks
- Distributed Storage
- Scalability
- Reputation Sharing
Cloud Applications
- Availability - Uptime, Cost, Single point failure, Scalability.
- Performance - Load balancer, auto scale, correct instances, etc.
- Security - CIA, authentication, encryption, etc.
- Disaster Recovery - RTO, RPO, Warm, Hot, Cold recovery.
NOTE
* This is short notes of the PPT, the main topics are covered above. Each point can be elaborated more as per the question.














Comments
Post a Comment