Design of Experiments (Unit 1)
Design of Experiments (Unit 1)
Design of experiments - DOE - Unit 1 - SRMIST 2022 syllabus.
Experiments
It is a series of conducted tests to analyse and understand behavioural patterns between certain factors and then to statistically predict outputs for future instances.
An experiment involves taking multiple tests by disturbing the environment and noting down the reaction. The goal is to make a test yield better outcome (efficiency) by optimizing the variable factors in the experiment.
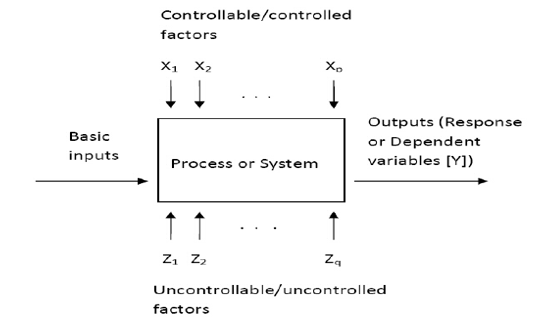
System Model
When basic inputs are fed into a process or system model, we expect an output from the process which is dependent on external factor which are either controllable or uncontrollable.
Objectives
- Determining the most influential control variables.
- Determining location of this variable for optimized output.
- The location of this variable must not lead to variable output.
- Effect of uncontrolled variable must be minimized.
Terms
- Response - Outcome of an experiment.
- Factors - Variables that affect the output of an experiment.
- Levels - The values of the factors.
- Treatment - Different sets of levels used in an experiment.
- Noise - Variables that affect / hinder performance of a test.
- Replication - Systematic duplication of an experiment.
Strategies
These strategies obtain unambiguous results at minimal cost while considering all factors. The performance level of each factor can be validated & hence we can obtain the most crucial factors that effect our response.
- One Factor at a time - a single unit of time for one factor
- Several Factors at a time - single unit of time for multiple factors
- Several factors at same time - multiple units of time for multiple factors
- Full factorial design - balanced time for factors without any biases
Steps in Experimentation
- Problem statement.
- Selection of factors, levels and ranges.
- Selection of response variables..
- Choice of design.
- Conducting experiment.
- Analysing of data.
- Conclusion & prediction.
DOE
A method to find the cause and effect of experiments. It determines the relationship between factors affecting the process and the output of the process.
Allows us to scientifically solve problems by selecting the proper experiment for the test. It also gives a proper understanding of the relationship between factors within an organization that wants to conduct an experiment.
Role of Experiments in DOE
- Exploration
- Estimation
- Confirmation
Industrial Usage
- Hypothesis
- Experiment
- Analysis
- Interpretation
- Conclusion
Success Criteria
- Planning skills - Finance, time, budget, expense and revenue.
- Statistical skills - Analysis, interaction of factors etc.
- Teamwork skills - Planning, skills, knowledge etc.
- Engineering skills - Range, level, factors, effect etc.
Principles
- Randomization - Experiments must not be under complete control.
- Replication - The experiments must be replicated for multiple takes.
- Blocking - Noise and unnecessary factors must be blocked.
- Degree of Freedom - Independent fair comparisons made.
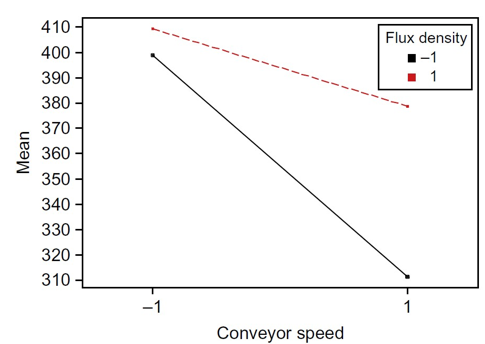
Interactions
Interactions allow understanding of different factors with one an other in an experiment. This way, certain factors can be optimized to get a desired output or to reduce competencies in an experiment.
Types
- Synergistic - Fixed or random effects which lead to factors not having a cross in their interaction. Either they are completely parallel or they do not meet until out of the given range of the experiment.
- Antagonistic - This would lead to a meet between factors in the given range of the experiment.
NOTE
* This article should be used as a mind map since it covers all the important topics in the PPT. Theory of each of the points mentioned above must be elaborated during the exam.
*If you are confident in your theory, this will help you score well.





Comments
Post a Comment