MAP Function in C++ STL
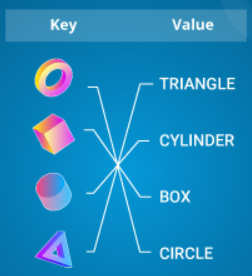
MAP Function in C++ STL The map function attributes values to certain keys. As can be seen above, the circle is matched with a circle, and so on. When the 'int' data type is attributed, the keys are automatically arranged in ascending order. The map can be manipulated in certain ways so that the value is always mapped to the key. So if you remove the key, the value is also removed. You move the key, and the value is also moved. Here is the syntax to create and display user-given inputs to a map. #include<bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std ; int main () { map< int , int > example ; int n , t1 , t2 ; cin>>n ; for ( int i= 0 ; i<n ; i++ ) { cin>>t1>>t2 ; ...


